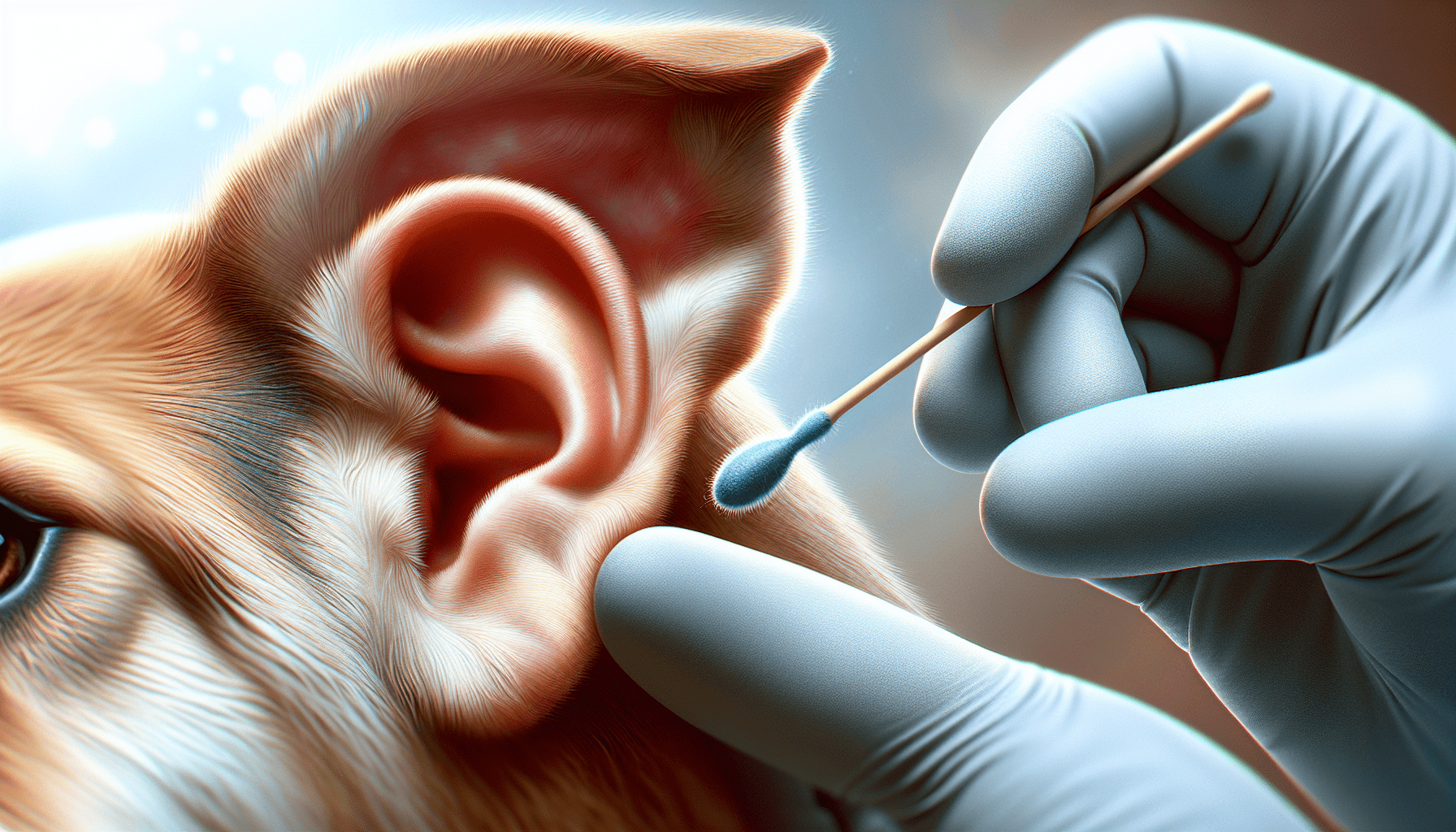
Have you ever noticed your dog scratching at their ears or shaking their head more than usual? If so, this behavior might indicate an ear infection. In this article, we’ll take a detailed look at ear infections in dogs, what causes them, how to prevent them, and the best ways to treat them. In addition, we’ll also discuss some other common health issues that dogs face to help you keep your furry friend in tip-top shape.
Common Dog Health Issues
Understanding common dog health issues can help you recognize problems early and seek appropriate treatment. Let’s explore some of the health concerns most pet owners encounter.
Skin Issues
Dogs often experience various skin problems. Symptoms might include scratching, chewing, and licking, while their skin could appear inflamed, red, flaky, or scaly.
Causes
Skin issues can stem from several sources, such as allergies, parasites, and bacterial or yeast infections. Environmental factors like pollen, mold, and even certain foods can trigger allergic reactions.
Prevention
Regular hygiene, thorough grooming, and including omega-3 supplements in your dog’s diet can help maintain healthy skin.
Treatment
Depending on the underlying cause, treatments might involve topical creams, ointments, and oral medications. Consulting your vet is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Ear Infections
Ear infections in dogs are a common yet treatable problem. Knowing the symptoms and causes can help you prevent and manage them effectively.
Symptoms
Watch for signs like ear scratching, head shaking, and ear discharge. These behaviors typically signal discomfort and infection.
Causes
Ear infections can be caused by:
- Bacteria
- Yeast
- Allergies
- Parasites
- Moisture build-up
Prevention
Regular ear checks and cleaning can prevent infections. Ensuring your dog’s ears are dry after bathing or swimming can also significantly reduce the risk.
Treatment
A thorough ear cleaning is often necessary, and in severe cases, this may need to be performed by a vet. Your vet might also prescribe medications like antibiotics or antifungal treatments.
Internal Parasites
Internal parasites are another common health issue. They can cause serious health problems if not addressed promptly.
Types of Internal Parasites
- Hookworms
- Roundworms
- Heartworms
- Tapeworms
- Whipworms
| Parasite | Symptoms | Prevention | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hookworms | Diarrhea, weight loss, anemia | Regular deworming, clean area | Medication prescribed by a vet |
| Roundworms | Vomiting, diarrhea, dull coat | Regular deworming, clean living areas | Vet-prescribed dewormers |
| Heartworms | Coughing, fatigue, weight loss | Heartworm preventive medications | Vet-administered heartworm treatment |
| Tapeworms | Visible segments in feces | Control fleas, regular deworming | Anti-tapeworm medication |
| Whipworms | Diarrhea, weight loss, bloody feces | Regular deworming, clean area | Vet-prescribed medication |
Prevention
Regular deworming, maintaining clean living spaces, and preventing exposure to snails and slugs can help protect your dog from internal parasites.
Treatment
Specific medications are required for different types of parasites, so seeking veterinary guidance for accurate diagnosis and treatment is essential.
External Parasites
External parasites like fleas, ticks, and mites can cause significant discomfort and health problems.
Types of External Parasites
- Fleas
- Ticks
- Mites
| Parasite | Symptoms | Prevention | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fleas | Itching, biting, red bumps | Preventive products, clean environment | Spot-on medications, oral meds |
| Ticks | Itching, visible attached ticks | Tick prevention treatments | Removal, topical treatments |
| Mites | Itching, hair loss, scabs | Cleaning environment, prevent interaction | Topical/ oral treatments |
Symptoms
If your dog is scratching, licking, or biting their skin and coat, they may be dealing with external parasites.
Prevention
Using preventive products regularly and maintaining a clean environment can help keep these pests at bay.
Treatment
Depending on the type of parasite, treatments might include spot-on medications, oral medications, or topical creams. Your vet can recommend an effective treatment plan.
Stomach Problems (Gastrointestinal Disorders)
Gastrointestinal disorders can range from mild to severe. Identifying symptoms early can help prevent more serious issues.
Symptoms
Common symptoms include diarrhea, constipation, vomiting, regurgitation, and general weakness.
Prevention
Maintaining a well-balanced diet, avoiding human food, and using probiotics can help prevent stomach problems.
Treatment
Treatment depends on the specific disorder and might include dietary changes, oral medications, and supplements. Proper diagnosis by your vet is essential.
Urinary Tract Infections (UTI)
Urinary Tract Infections can be uncomfortable for dogs and require timely treatment.
Symptoms
Symptoms of a UTI include bloody urination, frequent urination, and painful urination.
Causes
UTIs can be caused by parasites, bacteria, fungi, or diet.
Prevention
Regular potty breaks to encourage urination can help prevent UTIs.
Treatment
Treatment typically involves medication prescribed by a vet. Ensuring your dog completes the full course of antibiotics is important for effective treatment.
Overall Advice
Proactive care is essential to maintaining your dog’s health. Regular vet check-ups and an informed approach towards common symptoms can facilitate early detection and treatment. Here’s how you can keep your furry friend healthy:
- Regular Vet Check-Ups: Schedule routine health exams for early detection and management of potential health issues.
- Healthy Diet: Provide a well-balanced diet rich in nutrients and appropriate for your dog’s age, weight, and activity level.
- Proper Grooming: Regular grooming helps in early detection of skin problems and external parasites.
- Clean Environment: Keep your dog’s living area clean to prevent infections and parasites.
- Exercise and Mental Stimulation: Ensure your dog gets plenty of exercise and mental stimulation to maintain overall well-being.
Breed-Specific Concerns
Certain breeds are genetically predisposed to particular health issues. Being informed about your dog’s breed-specific health risks can support better prevention and care.
- Brachycephalic Breeds: Bulldogs, Pugs, and other short-nosed breeds are prone to breathing difficulties.
- Large Breeds: Great Danes, Mastiffs, and other large breeds may suffer from joint issues and heart problems.
- Small Breeds: Chihuahuas, Yorkshire Terriers, and other small breeds often face dental problems and hypoglycemia.
Consulting with your vet about your dog’s specific needs can help you prepare for potential health issues.
Conclusion
Ear infections in dogs, along with other common health issues such as skin problems, internal and external parasites, gastrointestinal disorders, and urinary tract infections, can significantly affect their well-being. By understanding these health concerns, you can take proactive steps to prevent and treat them timely. Regular veterinary care, a healthy diet, proper grooming, and a clean environment are keys to ensuring your dog lives a happy, healthy life. Keeping informed and being attentive to your dog’s needs will enable you to provide the best care possible.